How to prevent reflux esophagitis
One of the side effects of gastroesophageal reflux is esophagitis. It is often the first symptom of reflux itself, easily mistaken for colds. But it can be prevented.
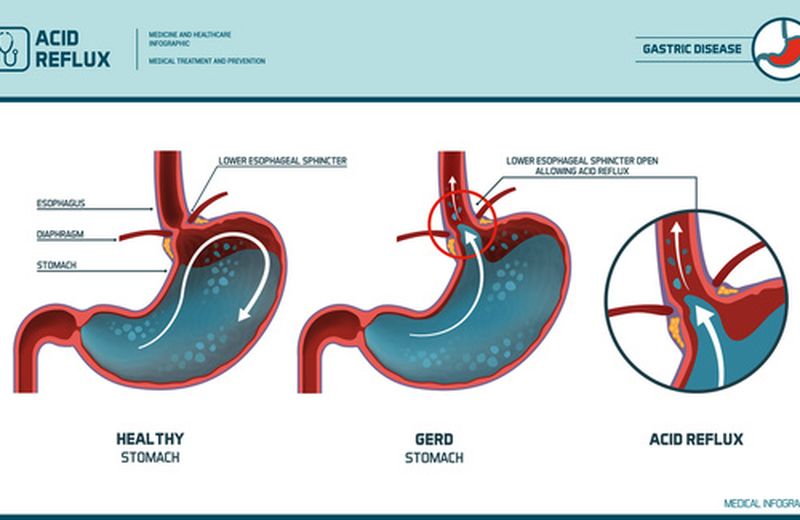
Gastroesophageal reflux can make life very… bitter in many ways.
Among the consequences of reflux there is inflammation of the esophagus or that part of the digestive system that food travels between the throat and the stomach. In fact, the esophageal mucosa is suitable for the transit of food that has yet to be digested and absolutely “unprepared” for the acidity of the liquids coming from the stomach , as in the case of reflux. If the phenomenon persists and becomes chronic, in the long run the mucous membranes become inflamed in contact with the acidic liquid, to the point of causing a real pathology or esophagitis , which manifests itself with symptoms such as burning in the stomach or behind the breastbone or nonspecific symptoms, such as hoarseness or chronic cough.
Preventing reflux esophagitis involves a series of measures aimed at decreasing reflux. Which?
Read also Gastric reflux, natural remedies >>
Reflux esophagitis: prevent with food
To prevent reflux esophagitis it will be good to maintain an adequate diet , free of foods that are difficult to digest or that increase gastric secretion.
In detail, in the case of reflux esophagitis, these are the foods to be eliminated :
> All fried foods;
> Ready -made dishes (in the preparation of which a lot of fats of various origins are used);
> Sauces, ragu and sauces prepared with abundant quantities of oil, margarine, butter, lard;
> Desserts with creams and cream ;
> All very cooked meats , in all forms: stews, goulash, boiled;
> All visible fat present on meat and cold cuts;
> All spirits .
In the case of acute esophagitis , whether or not caused by reflux, it will also be good to limit the consumption of foods that can aggravate inflammation of the esophageal mucosa, such as:
With the exception of everything that can harm your esophagitis, here are the foods to be preferred to prevent reflux and the resulting esophagitis:
> Water, preferably between meals, not less than 1.5 liters per day;
> Whole grains;
> Fresh and seasonal fruit and vegetables;
> Skimmed or partially skimmed milk or yogurt, low-fat and light cheeses;
> White meat chicken, turkey, rabbit;
> Low fat fish such as: sea bass, sole, sea bream, cod;
> Eggs not fried;
> Extra-virgin olive oil added raw.
Read also Nocturnal gastroesophageal reflux, what to do >>
Reflux esophagitis: preventing with good habits
Nutrition alone may not be enough to prevent gastroesophageal reflux esophagitis .
In fact, lifestyle changes and the acquisition of some “virtuous behaviors” will be necessary, such as:
To avoid:
> large meals, prefer small and frequent meals;
> foods and drinks that are too hot or too cold;
> the excess of liquids during meals, so as not to dilute the gastric juices by slowing down digestion.
> Drink at least 1.5 liters of water, sipped slowly throughout the day. Saliva and liquids protect the esophageal muscles from gastric juices
> Stop smoking as, in addition to other damage, a large amount of air is introduced which can promote reflux
> Eat slowly, chew bites of food calmly . Eating hastily by swallowing whole bites promotes reflux as it lengthens the residence time of food in the stomach
> Do not wear belts or clothes that are very tight at the waist because they increase the pressure on the abdomen, facilitating reflux.
> No to nap! Avoid lying down immediately after meals to avoid reflux. After eating, you should wait at least two or three hours before going to bed. A walk can be much more useful for digesting
> No sports after lunch . Avoid exercising on a full stomach , especially exercises that engage the abdominal muscles.
> Sleeping with a pillow under your back. Raising the front of the bed 10-15cm helps keep the esophagus upright even when lying down and prevents acidic material from rising from the stomach. Avoid using piles of pillows, as they force you into a position that increases pressure on the abdomen.
> Lose weight. Gradually reduce weight and abdominal circumference , through a balanced low-calorie diet and regular physical exercise.
> No chewing gum. The habit of chewing gum directly increases the amount of air present in the gastric pouch. The presence of these gases increases the pressure inside the stomach, promoting reflux
> Beware of drugs that can be harmful to the esophageal mucosa such as NSAIDs (aspirin, ibuprofen), some sedatives and tranquilizers, etc. In any case, it is advisable to communicate their use to your doctor, in order to check their compatibility with the disease and find, if necessary, less invasive alternatives.




























+ There are no comments
Add yours