Becoming an osteopath: training and profession
In Italy, the osteopath is a poorly protected professional. Years of study and training to become an osteopath are not enough for full professional recognition. But who is the osteopath and how does osteopathy actually act on the well-being of the person?
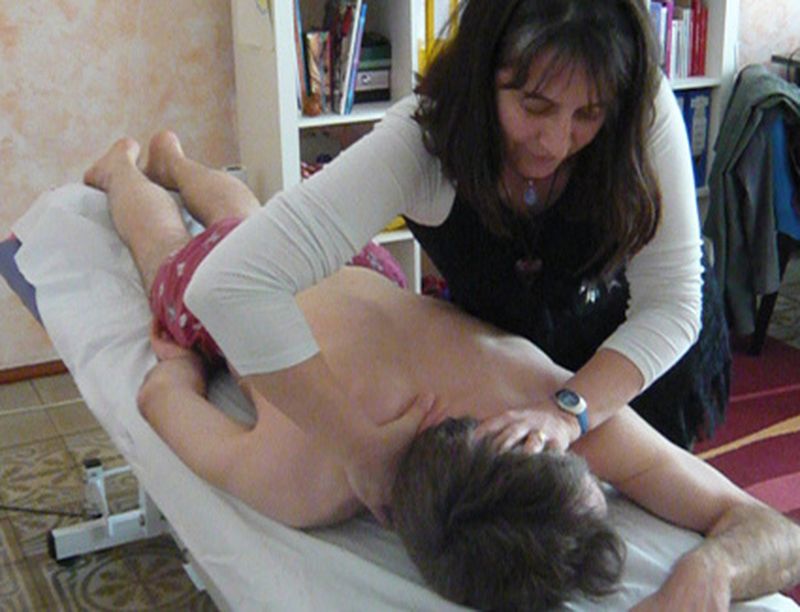
The osteopathic discipline
Anyone who wants to become an osteopath decides to undertake manual therapy , complementary to classical medicine. This natural method does not involve the use of drugs and uses a causal and not symptomatic approach . That is, it studies the individual as a whole and is not satisfied with solving the symptom, but goes in search of the cause that can also find its localization in another area than that of the pain. It is effective for the prevention, evaluation and treatment of disorders affecting the neuro-musculoskeletal system, which can however be associated with functional alterations of the organs and viscera and of the craniosacral system.
In osteopathy the individual is seen as a whole as a system composed of muscles, skeletal structures, internal organs that find their connection in the nerve centers of the spinal column. Each constituent part of the person (including the psyche) is dependent on the others and the correct functioning of each ensures that of the entire structure: therefore, well-being. Now let’s see who the osteopathic practitioner is and how he works.
The profession of the osteopath
In osteopathy, it is not the therapist who heals, but his role is to eliminate the “obstacles” to the body’s ways of communication , in order to allow the organism, by exploiting its own self-regulation phenomena, to achieve healing. Osteopathy aims to restore the harmony of the skeletal support structure in order to allow the body to find its own balance and well-being. Becoming an osteopath therefore presupposes the main objective of restoring a correct balance of the body through various manipulative approaches that in most of the times do not affect the pain area. The osteopath, through the use of a variety of manual and non-manual techniques, restores and relaunches joint movement, visceral and fascial, stimulating and facilitating the mechanisms of self-regulation , body adaptation and restoration of homeostasis.
How does an osteopath work? The consultation begins with an anamnesis that starts from the patient’s main disorder, and then goes back to the osteopathic lesion (s) involved in the problem (integrated in its entirety). Its goal is to diagnose, with the help of clinical and osteopathic tests, the mobility and elasticity / deformability barriers of the anatomical structures that can limit the organism in its physiological functions. This procedure will allow him to develop an appropriate treatment. To this end, he will use structural or functional manual techniques on all the structures of the locomotor system (ligaments, muscles, fascias, bones, etc.), visceral and craniosacral . In addition to the possibility of opening your own clinic, the osteopath can collaborate with other health professionals, and in particular in various specialized fields of conventional medicine. The areas of intervention concern the supporting structure of the organism and all the connections within it and with the contiguous systems, such as orthopedics, otolaryngology, odontostomatology, pediatrics, ophthalmology, geriatrics, urology, gastroenterolology, cardiology, endocrinology and gynecology). But what to do to become an osteopath?
READ ALSO The osteopath: laws and professional requirements i
What to do to become an osteopath
To become an osteopath, a six-year training course is required which includes the study of basic medical sciences such as anatomy, pathology, physiology, biomechanics, biochemistry, biophysics, embryology, histology, neurology and others, in addition to purely osteopathic subjects. Training in Italy is not continuous and is not university-based, but private. There are several schools of osteopathy in the area that organize osteopathy courses.
The Ministry of Health does not issue a license to practice the profession of osteopath . The practice turns out to be enabling only if the osteopath is already in possession of a previous medical qualification (surgeon, dentist or physiotherapist). Otherwise, the professional title is invalid . The lack of a juridical status for osteopathy has, by objective necessity, required the establishment of professional associations that strive to obtain not only legal recognition of osteopathy, but also regulation and protection of the osteopathic profession .
The lack of rules that regulate its exercise means that the professional figure of the osteopath is not protected by the law, and therefore that anyone is allowed to practice it, to the detriment of osteopaths but above all of patients. The main Italian regulatory association is the Superior Council of Osteopathy (CSdO), made up of the major associations of osteopathic professionals present on the national territory.
In the United States, where it was born, osteopathy entered public health in 1991. In the United States, osteopaths are general practitioners , medical graduates, and can claim the title of doctor. In England, Canada, Australia and New Zealand, osteopaths do not have medical degrees. In most of Europe, including Italy, there are osteopathic institutes, but there is still no official recognition , even if there are ad hoc proposals in this regard .




























+ There are no comments
Add yours